Group-A
Syllabus (A)Binomial Theorem (Unit-1)
Trigonometry (Unit-2)
Differential Equations
Vectors Parallelogram law of vectors: The parallelogram law of vectors is a method for adding two vectors graphically to find their resultant vector. The law states that if two vectors are represented by two adjacent sides of a parallelogram, then the diagonal passing through their point of intersection will be equal in magnitude and direction to the resultant of the two vectors. In other words, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the four sides of the parallelogram is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two diagonals of the parallelogram. 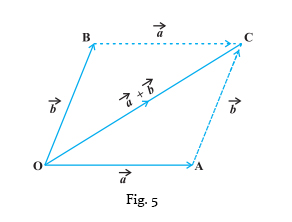
- Find the resultant vector of two vectors, one with magnitude 5 and angle 30 degrees and the other with magnitude 7 and angle 150 degrees.
- A plane is flying with a velocity of 200 km/h at an angle of 30 degrees with respect to the ground. A wind is blowing at a speed of 50 km/h in a direction perpendicular to the plane’s path. What is the resultant velocity of the plane?
- Two people are pushing a box, one with a force of 30 N to the right and the other with a force of 40 N to the left. What is the net force on the box?
- A boat is traveling with a velocity of 10 m/s at an angle of 45 degrees with respect to the current. The current has a velocity of 5 m/s in a direction perpendicular to the boat’s path. What is the resultant velocity of the boat?
- Two vectors, A and B, have magnitudes of 5 and 7, respectively, and an angle of 60 degrees between them. What is the magnitude of their resultant vector?
- A person walks 3 km north, then 4 km east, and finally 2 km south. What is the person’s displacement?
- A car travels 100 km north, then 200 km east, and finally 300 km south. What is the car’s displacement?
- Two forces, one with magnitude 10 N and angle 30 degrees and the other with magnitude 5 N and angle 150 degrees, act on an object. What is the magnitude and direction of the resultant force on the object?
- A football is kicked with an initial velocity of 20 m/s at an angle of 45 degrees with respect to the ground. What is the horizontal and vertical component of the velocity?
- A helicopter is flying with a velocity of 150 km/h at an angle of 60 degrees with respect to the ground. What is the horizontal and vertical component of the velocity?
- Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector formed by adding vectors A = 3i + 4j and B = -2i + 6j.
- A car moves 20 km north, then 30 km east. Find the magnitude and direction of its displacement from the starting point.
- Vector A has magnitude 5 and direction 30 degrees from the positive x-axis, while vector B has magnitude 3 and direction 120 degrees from the positive x-axis. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
- A force of 50 N is applied to an object at an angle of 30 degrees from the horizontal, while another force of 75 N is applied to the object at an angle of 150 degrees from the horizontal. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.
- A person walks 5 km due north, then turns and walks 3 km due east. If the person then walks 4 km due south and finally turns and walks 2 km due west, find the magnitude and direction of the person’s resultant displacement from the starting point.
- A force of 100 N is acting at an angle of 60 degrees and a force of 150 N is acting at an angle of 120 degrees. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force acting on the body.
- A displacement of 20 m is made in the east direction, followed by a displacement of 15 m in the north direction. What is the resultant displacement of the object?
- Two vectors A and B have a magnitude of 10 N and 12 N, respectively, and they are inclined at an angle of 30 degrees with each other. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
- A ship is moving at a speed of 30 km/h towards the northeast and a current is flowing in the east direction at a speed of 10 km/h. Find the speed and direction of the ship relative to the water.
- A car is traveling at a speed of 40 km/h towards the east and a wind is blowing towards the north at a speed of 10 km/h. Find the resultant velocity of the car.
- Two forces of magnitudes 8 N and 15 N act on a body at an angle of 60° to each other. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.
- Two vectors A and B have magnitudes 7 and 9 units respectively. If the angle between them is 45°, find the magnitude and direction of their sum.
- A boat moves with a velocity of 10 km/h in a direction making an angle of 30° with the current which flows at 6 km/h. Find the resulting velocity of the boat.
- A car moves 30 km due east and then 40 km due north. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement.
- Three forces, each of magnitude 10 N, act on a point in directions that are mutually perpendicular. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.
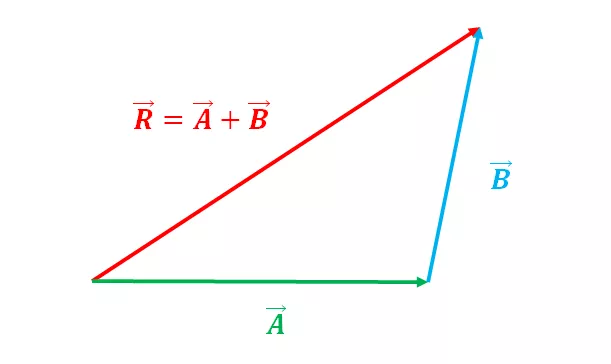
- Suppose you walk 10 meters east, then turn and walk 15 meters north. Your total displacement can be found by drawing a triangle with sides of 10 meters and 15 meters. The diagonal of the triangle represents your total displacement.
- If you are flying in an airplane and the wind is blowing from the southwest at 30 knots, while your plane is moving at 200 knots due north, the plane’s total velocity can be found by drawing a triangle with sides of 30 knots and 200 knots. The diagonal of the triangle represents the plane’s total velocity.
- If a boat is traveling at 15 knots due east, and there is a current pushing the boat at 5 knots due south, the boat’s total velocity can be found by drawing a triangle with sides of 15 knots and 5 knots. The diagonal of the triangle represents the boat’s total velocity.
Thanks Sir
Ok
Hi sir
Hii sir
Hiii sir 11 bajane wala hai Question upload kar dijiye